Weave supports logging and displaying video, images, and audio.
Video
Weave automatically logs videos using moviepy. This allows you to pass video inputs and outputs to traced functions, and Weave will automatically handle uploading and storing video data.
Video support is currently only available in Python.
Images
Logging type: PIL.Image.Image.
Base64-encoded image strings (e.g., data:image/jpeg;base64,...) are technically supported but discouraged. They can cause performance issues and should only be used if absolutely necessary (e.g., for integration with specific APIs).
import weave
from openai import OpenAI
import requests
from PIL import Image
weave.init('image-example')
client = OpenAI()
@weave.op
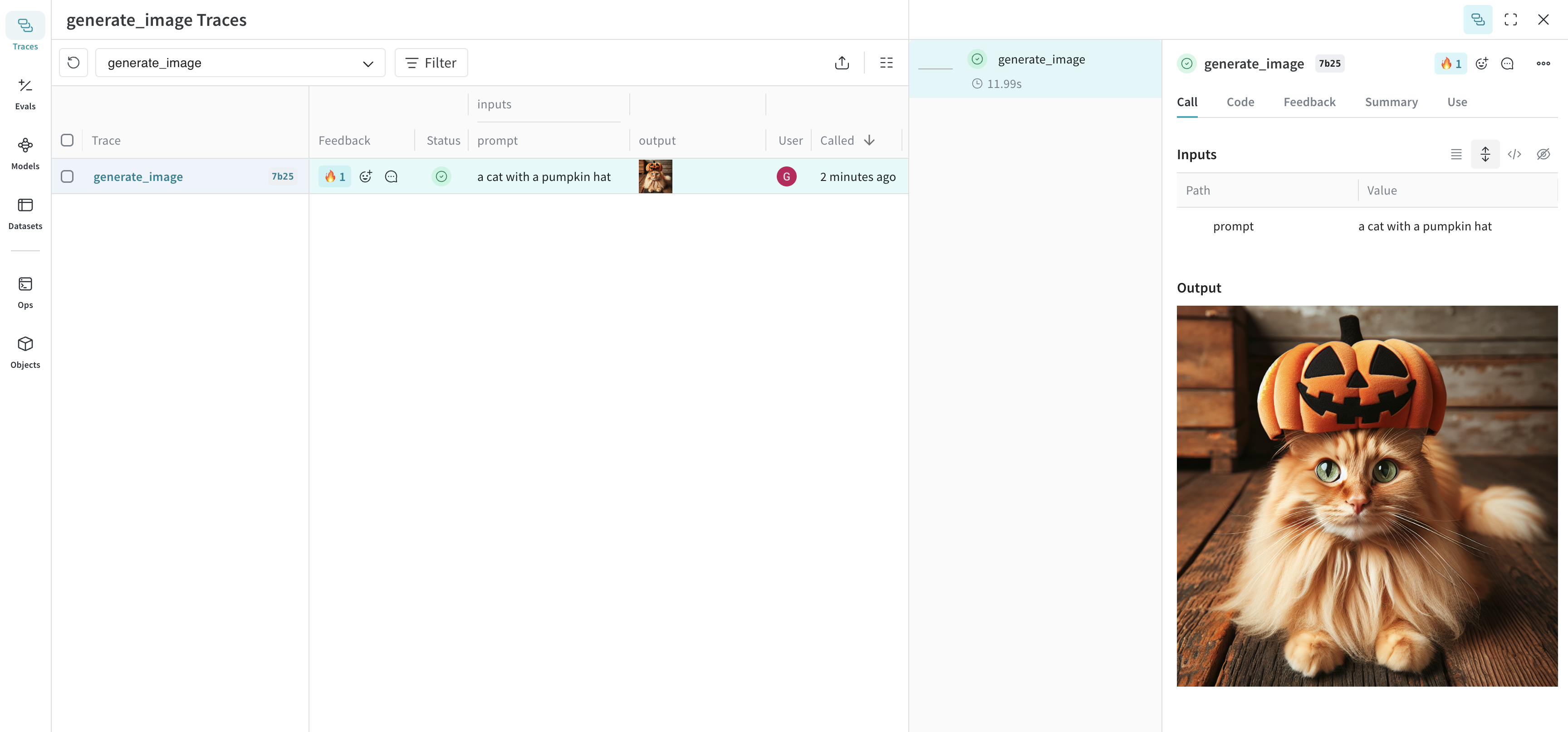
def generate_image(prompt: str) -> Image:
response = client.images.generate(
model="dall-e-3",
prompt=prompt,
size="1024x1024",
quality="standard",
n=1,
)
image_url = response.data[0].url
image_response = requests.get(image_url, stream=True)
image = Image.open(image_response.raw)
# return a PIL.Image.Image object to be logged as an image
return image
generate_image("a cat with a pumpkin hat")
import {OpenAI} from 'openai';
import * as weave from 'weave';
async function main() {
const client = await weave.init('image-example');
const openai = new OpenAI();
const generateImage = weave.op(async (prompt: string) => {
const response = await openai.images.generate({
model: 'dall-e-3',
prompt: prompt,
size: '1024x1024',
quality: 'standard',
n: 1,
});
const imageUrl = response.data[0].url;
const imgResponse = await fetch(imageUrl);
const data = Buffer.from(await imgResponse.arrayBuffer());
return weave.weaveImage({data});
});
generateImage('a cat with a pumpkin hat');
}
main();
Resize large images before logging
It can be helpful to resize images before logging to reduce UI rendering cost and storage impact. You can use postprocess_output in your @weave.op to resize an image.
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Any
from PIL import Image
import weave
weave.init('image-resize-example')
# Custom output type
@dataclass
class ImageResult:
label: str
image: Image.Image
# Resize helper
def resize_image(image: Image.Image, max_size=(512, 512)) -> Image.Image:
image = image.copy()
image.thumbnail(max_size, Image.ANTIALIAS)
return image
# Postprocess output to resize image before logging
def postprocess_output(output: ImageResult) -> ImageResult:
resized = resize_image(output.image)
return ImageResult(label=output.label, image=resized)
@weave.op(postprocess_output=postprocess_output)
def generate_large_image() -> ImageResult:
# Create an example image to process (e.g., 2000x2000 red square)
img = Image.new("RGB", (2000, 2000), color="red")
return ImageResult(label="big red square", image=img)
generate_large_image()
Audio
Logging type: wave.Wave_read.
The following example shows how to log an audio file using OpenAI’s speech generation API.
import weave
from openai import OpenAI
import wave
weave.init("audio-example")
client = OpenAI()
@weave.op
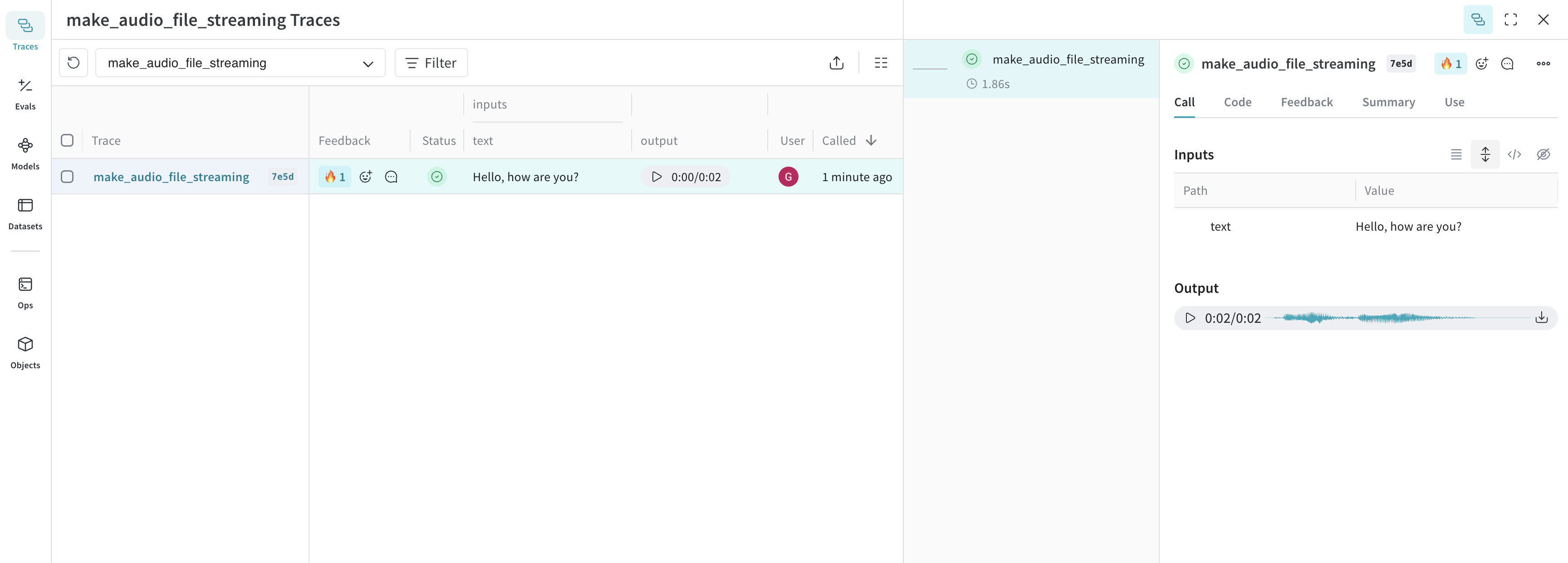
def make_audio_file_streaming(text: str) -> wave.Wave_read:
with client.audio.speech.with_streaming_response.create(
model="tts-1",
voice="alloy",
input=text,
response_format="wav",
) as res:
res.stream_to_file("output.wav")
# return a wave.Wave_read object to be logged as audio
return wave.open("output.wav")
make_audio_file_streaming("Hello, how are you?")
import {OpenAI} from 'openai';
import * as weave from 'weave';
async function main() {
await weave.init('audio-example');
const openai = new OpenAI();
const makeAudioFileStreaming = weave.op(async function audio(text: string) {
const response = await openai.audio.speech.create({
model: 'tts-1',
voice: 'alloy',
input: text,
response_format: 'wav',
});
const chunks: Uint8Array[] = [];
for await (const chunk of response.body) {
chunks.push(chunk);
}
return weave.weaveAudio({data: Buffer.concat(chunks)});
});
await makeAudioFileStreaming('Hello, how are you?');
}
main();
Try our cookbook for Audio Logging or 
Open in Colab



